Introduction to the Algorithm
MEWS is an algorithm that takes as its input serial vital signs, performs a computation, and predicts which patients will decompensate (deteriorate), thereby providing an actionable alert enabling collaboration among the rapid response team (RRT) and the bedside nurse.
The MEWS application provides for:
- Another layer of surveillance
- Additional eyes on a potentially ill patient
- Skill Development for the bedside nurse
- Prevention of unplanned admissions to ICU and death
Application Roadmap
The RADS2 team has implemented the generation of MEWS score in real-time with the following features:
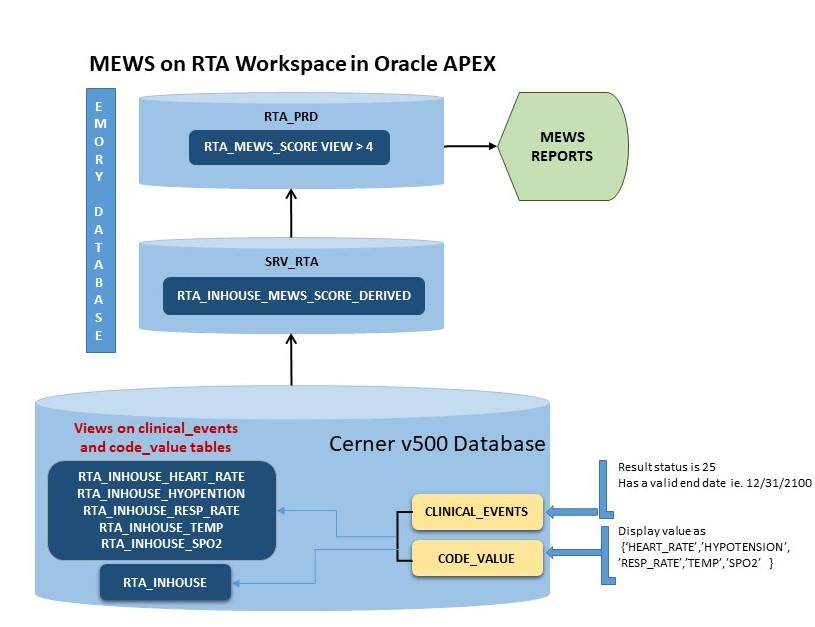
- MEWS application returns the Heart Rate, SaO2, Respiratory Rate, Hypotension, Urine output, Temperature values to determine the MEWS score
- If the total score >4 then it sends the list of the patients at risk of clinical decompensation to the nurses
- MEWS scores are cached every 10mins to provide the most recent Real Time Data
A pilot study is ongoing on 4 units where the rapid response team interacts with the patient and bedside nurse when a threshold score is triggered in order to assist in providing early interventions with the goal of preventing further decompensation.
The EWS envisioned by the RADS2 would further personalize the system (Personalized EWS or PEWS), enabling it to fire in response to each patient’s unique pathophysiology, taking into consideration individual patient’s “Set Points”.
As part of the envisioned EWS, following are the additional features that are being considered for the MEWS application:
- Alerting mechanisms triggered upon deterioration of patient condition
- Information as to what triggered the alert
- Inclusion of device, conventional EMR and derived data to personalize the MEWS
- Post discharge monitoring of the patient
- Making the MEWS algorithm scores available to the bedside nurses and providers without having to login to external systems
Design and Implementation
The Cerner EMR database is the source for clinical events relating to heartrate, hypotension, respioratory rate, temperature and oxygen saturation for a patient. We have created database views that capture these events and stored procedures that calculate the MEWS score from the data in these views. This information is pulled into the RTA production database every 10 minutes.
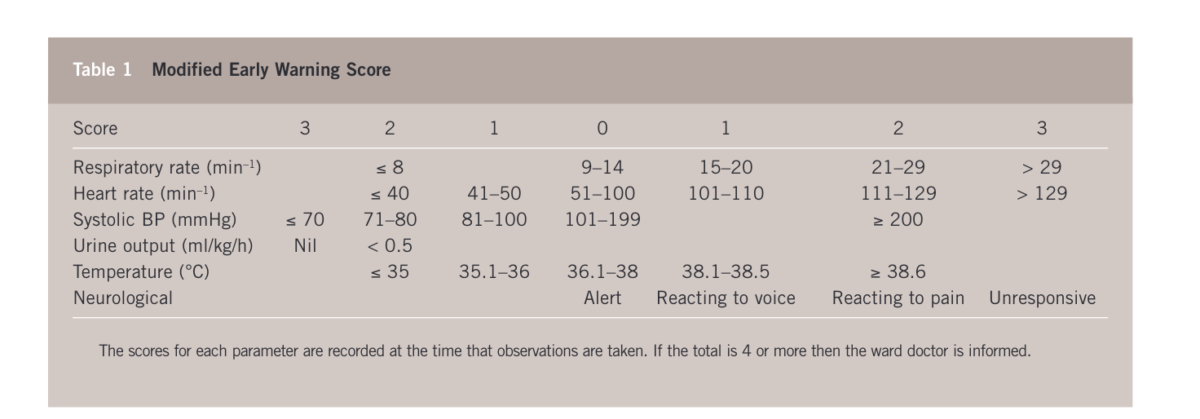
Scoring System Details
The following table shows the system followed generated scores for the application: