One of the key goals of the EASIL program is to publish research findings and train the next generation of antibiotic stewards in both academia and in the clinic.

Publications
Variation in Measures of Antimicrobial Use Across Four Nursing Homes, Atlanta, Georgia, 2019
Dube, W. et al., 2020: Decennial Abstracts
Background: Although antibiotic stewardship programs (ASP) are now required in nursing homes, assimilating and responding to data to improve prescribing in nursing homes is novel. Four Atlanta-based skilled nursing facilities (SNFs) began collaborating (EASIL: Emory Antibiotic Stewardship in Long-Term Care) to share standardized prescribing data to allow interfacility comparisons and action.
Creating reasonable antibiograms for antibiotic stewardship programs in nursing homes: Analysis of 260 facilities in a large geographic region, 2016–2017
Fridkin, SK. et al., 2019: Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology
Objective: To determine the best nursing home facility characteristics for aggregating antibiotic susceptibility testing results across nursing homes to produce a useful annual antibiogram that nursing homes can use in their antimicrobial stewardship programs.
Evaluation of Care Interactions Between Healthcare Personnel and Residents in Nursing Homes Across the United States
Chang, NC. et al., 2020: Decennial Abstracts
Background: Certain nursing home (NH) resident care tasks have a higher risk for multidrug-resistant organisms (MDRO) transfer to healthcare personnel (HCP), which can result in transmission to residents if HCPs fail to perform recommended infection prevention practices. However, data on HCP-resident interactions are limited and do not account for intrafacility practice variation. Understanding differences in interactions, by HCP role and unit, is important for informing MDRO prevention strategies in NHs.
Mentoring
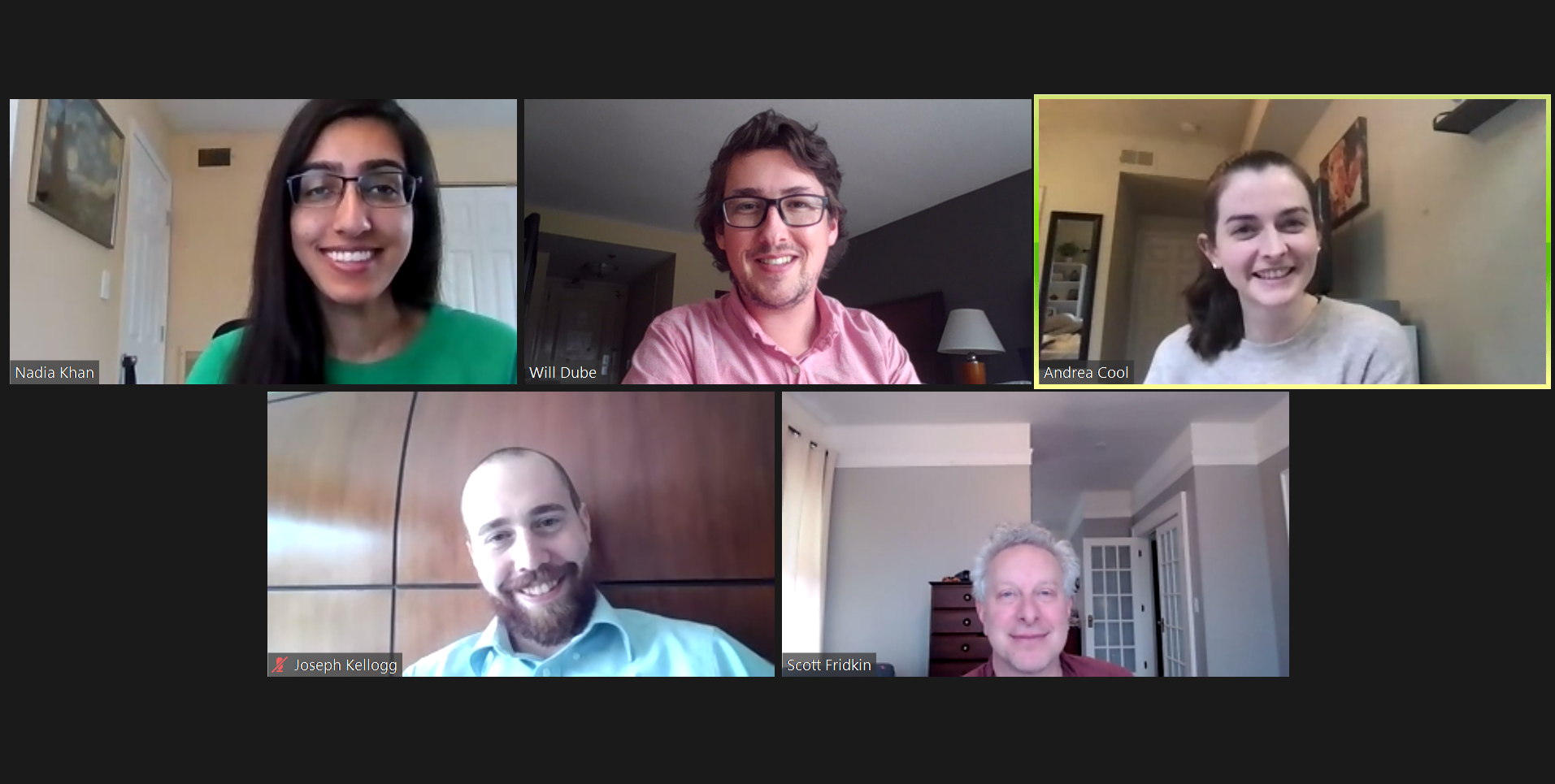
Thesis Manuscript: Changes in antibiotic prescribing metrics at 3 nursing homes in Atlanta collaborating on antibiotic stewardship
Cool, A. et al., 2020
Summary: Antibiotic overuse can contribute to antibiotic resistance and adverse events. Results showed some improvements in UTI antibiotic prescribing. Exploring how effects may vary due to implementation differences is warranted.
Meet the Team