This Common Drug Could Help People with Depression Feel Motivated Again

November 18, 2025 | Knowridge
Dr. Andrew Miller, another researcher on the team, explained that treating the root cause – inflammation – could offer better long-term help for patients. | Read More
Chronic Inflammation Messes with Your Mind. Here's How to Calm It
August 18, 2025 | NewScientist
Golam Khandaker’s mother has had arthritis for as long as he can remember. She also lives with depression, and it always struck Khandaker how precisely her arthritis flare-ups coincide with her most severe episodes of low mood. | Read More
Emory Researchers Call for an Inflammatory Subtype of Major Depression, Paving the Way for Precision Psychiatry

June 4, 2025 | Emory News Center
Researchers at Emory University have provided compelling evidence supporting the existence of an inflammatory subtype of major depression, a breakthrough that could transform how this complex disorder is diagnosed and treated. Led by Andrew H. Miller, MD — a pioneer in inflammation research related to depression — Emory investigators highlight inflammation as a key driver of depressive symptoms in approximately 25 to 30% of patients. Their work is featured in three recent journal publications. | Read More | Medical Xpress
Levodopa May Improve Motivation in Depression Linked to High Inflammation
March 19, 2025 | Emory News Center
A study from Emory University suggests that levodopa, a medication that increases dopamine levels in the brain, may help treat individuals with depression who experience motivational impairments due to high inflammation. Researchers found that a common blood test measuring C-reactive protein, a blood biomarker of inflammation produced by the liver, could help determine which patients are most likely to respond to repeated doses of levodopa. | Read More
Prominent Researchers Call for Critical Overhaul of Psychiatric Drug Development and New Approaches to Anti-Inflammatory Treatments

April 5, 2024 | Emory News Center
Many studies have found that inflammation contributes to several psychiatric disorders but developing drugs that target inflammation as a treatment for these conditions is proving to be difficult. Clinical trials using anti-inflammatory drugs to treat depression and schizophrenia for example have had limited success, and there is great risk that these drugs will be abandoned altogether. | Read More
How Inflammation in the Body May Explain Depression in the Brain

February 23, 2023 | Washington Post
Dr. Andrew Miller describes the impact of inflammation on our brains and livelihoods – and steps we can take to minimize it. But how inflammation influences depression is complex. Inflammation may be increasing anhedonia, or the depressive symptom of reduced pleasure. | Read More
A Drug that Increases Dopamine can Reverse the Effects of Inflammation on the Brain in Depression, Emory Study Shows
January 26, 2023 | Emory News Center
An Emory University study published in Nature’s Molecular Psychiatry shows levodopa, a drug that increases dopamine in the brain, has potential to reverse the effects of inflammation on brain reward circuitry, ultimately improving symptoms of depression. Numerous labs across the world have shown that inflammation causes reduced motivation and anhedonia, a core symptom of depression, by affecting the brain’s reward pathways. | Read More
Is Inflammation the Link Between Cancer and Depression—and Can We Screen for it?

May 2, 2022 | Winship Cancer Institute
Depression is common in patients with cancer and is associated with poor quality of life and worse disease outcomes. A first-ever systematic review and meta-analysis of earlier studies has found that certain measurable indicators of inflammation typically found in patients with cancer may provide a useful, screenable indication as to which of them may be at risk for depression. | Read More
Researchers Outline the Connection Between Inflammation and Depression

October 25, 2021 | Emory News Center
In a paper published recently in Pharmacological Reviews, Emory University School of Medicine researchers outlined the impact of inflammation on motivation as it relates to depression. The researchers propose that low grade inflammation affects brain chemicals and brain circuits that regulate motivation, ultimately leading to motivational deficits and a loss of interest or willingness to engage in usually pleasurable activities including work and play. These motivational deficits are reflected as anhedonia, a core and likely the most disabling symptom of depression, as well as other psychiatric disorders. | Read More
Cancer Treatments May Accelerate Cellular Aging

May 24, 2021 | Eurekalert!
New research indicates that certain anti-cancer therapies may hasten cellular aging, where changes in the DNA of patients may contribute to greater inflammation and fatigue. The findings are published by Wiley early online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society. | Read More
High Levels of Inflammation and Blood Glucose May Contribute to Anhedonia in MDD
May 12, 2020 | Psychiatry Advisor
High blood glucose levels coupled with low tyrosine metabolism may identify patients with depression, who have increased inflammation and higher rates of anhedonia, according to a study published in Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. Additionally, the study reported that anhedonia with high C-reactive protein, a marker for inflammation, may involve immunometabolic shifts as well as reduced availability of dopamine precursors in patients in major depressive disorder. | Read More
Can Anti-Inflammatory Strategies Light Up the Dim Depression Pipeline?

March 18, 2020 | Nature
Microglia: A New Target in the Brain for Depression, Alzheimer’s and More?
January 20, 2020 | STAT
At Emory University School of Medicine, researchers have found that inflammation is linked to weakened reward circuits in depression — and they can predict which patients’ neural circuits are going dark by measuring their level of inflammation via a simple blood draw. Also underway at Emory are clinical trials looking at the viability of using the same anti-inflammatories employed to treat autoimmune disease, such as infliximab, to treat depression. The hope is that by getting overexcited microglia to back off, important regions of the brain will be able to communicate again. | Read More
Inflammation is Aging Your Brain

December 2, 2019
Dr. Andrew Miller spoke with Dave Asprey on his podcast, Bulletproof Radio, to discuss inflammation’s effects on aging. | Listen Here
Science Says This is How Stress Kills Your Motivation

June 11, 2019 | Inc
But scientists from Emory University now say that chronic inflammation is a huge troublemaker, and that it might interfere with your drive to persist and explore. According to their new theory, detailed in the paper Can’t or Won’t? Immunometabolic Constraints on Dopaminergic Drive, chronic inflammation puts a squeeze on your brain’s dopamine supply. The authors--Michael Treadway, Andrew Miller, and Jessica Cooper--say the problem between inflammation and motivation is actually a sophisticated protective mechanism that forces you to cool it. | Read More
Does Chronic Inflammation Reduce Motivation?

June 6, 2019 | Psychology Today
Inflammation has been a front-of-mind nemesis for as long as I can remember. Back in the days when I competed in extreme distance races, minimizing proinflammatory cytokines and "the inflammatory reflex" was always a top priority. As an athlete and coach, I knew from scientific literature (Dinarello, 2000; Tracey, 2002) and road-tested experience that inflammation impeded sports performance and hampered recovery. | Read More
How Chronic Inflammation May Drive Down Dopamine and Motivation

June 4, 2019 | Medical Xpress
Growing evidence shows that the brain's dopamine system, which drives motivation, is directly affected by chronic, low-grade inflammation. A new paper proposes that this connection between dopamine, effort and the inflammatory response is an adaptive mechanism to help the body conserve energy. | Read More
Next-Generation Antidepressants Show Promise for Treatment-Resistant Disease

May 19, 2019 | Healio
Andrew Miller, MD, professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, Emory University, discussed the mechanisms and treatment implications of inflammation and treatment-resistance in depression. Data suggest there’s a link between inflammation and depression. Miller said that depressed patients show all the “carbon features” of a chronic inflammatory response with increases of inflammatory cytokines (like interleukin 6 and acute phase reactants. | Read More
Can My Dentist Cure Depression?
February 23, 2019 | Psychology Today
In fact, inflammation affects neural systems and behavior in very specific ways, most notably by interfering with motivation, motor activity, arousal, anxiety and sensitivity to threat, as outlined by Andrew Millar - a Professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory University School of Medicine. | Read More
HPV Status of Head, Neck Cancer Influences Fatigue, Inflammation
July 17, 2018 | Healio
Patients with HPV-unrelated squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck experienced greater fatigue and inflammation at baseline and over time than patients with HPV-related tumors, according to results of a longitudinal, prospective study. However, patients with HPV-related tumors experienced a greater increase in fatigue during the first month of radiotherapy. | Read More
The Brave New World of Inflammation

July 5, 2018 | Psychiatric Times
The Inflammation Connection: Most of our prior and current preconceptions about the role of immunity and mental illness have been-and are-wrong. Special Report Chair Charles Raison, MD, introduces clinicians and researchers to a collection of cutting-edge information on inflammation and psychiatry. Scroll through the slides for links to each report. | Read More
Study Identifies a Link Between Antidepressant Treatment Resistance and Inflammation
June 11, 2018 | Medical Xpress
Researchers at Emory University have found that depressed patients who have not responded to multiple antidepressants exhibit evidence of increased inflammation. Findings were recently published online in the journal, Psychoneuroendocrinology. | Read More
Peripheral Inflammatory Markers are Associated with Psychomotor Retardation in Major Depressive Disorder

June 22, 2016 | Psychiatry Advisor
Major depressive disorder has the highest lifetime prevalence of any neuropsychiatric disorder and is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Currently available antidepressant medications fail to treat a significant number of patients. | Read More
Could a Drug that Tamps Down Inflammation Lift the Fog of Depression?
January 28, 2016 | STAT
One of the world’s largest drug makers is testing a radical new approach to treating depression — by dialing down inflammation in the body, rather than tinkering with chemicals in the brain. | Read More
Inflammation Increases Glutamate to Cause Depression?
January 13, 2016 | Neuroscience News
Psychiatrists investigating depression have been energized in recent years by reports of rapid, successful treatment with drugs that interfere with the brain chemical glutamate, such as the anesthetic ketamine. New research from Emory University School of Medicine is providing hints as to which forms of depression may respond best to drugs that target glutamate. | Read More | Science Daily
The Role of Inflammation in Depression: from Evolutionary Imperative to Modern Treatment Target

December 29, 2015 | Nature
Crosstalk between inflammatory pathways and neurocircuits in the brain can lead to behavioural responses, such as avoidance and alarm, that are likely to have provided early humans with an evolutionary advantage in their interactions with pathogens and predators. | Read More
Inflammation Linked to Weakened Reward Circuits in Depression

November 20, 2015 | Emory University
About one third of people with depression have high levels of inflammation markers in their blood. New research indicates that persistent inflammation affects the brain in ways that are connected with stubborn symptoms of depression, such as anhedonia, the inability to experience pleasure. | Read More | Yahoo! News
Researchers Consider Infection as One Cause of Depression
March 20, 2015 | Psychiatry Online
Could major depressive disorder be the outcome of an infectious disease? However, most infections that lead to behavioral changes don’t do so by directly infecting the brain, said Andrew Miller, MD, a professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Emory School of Medicine and an expert on brain-immune interactions. “We can’t seem to find an agent that’s reliably associated with psychiatric disorders that is not also found in healthy persons.” | Read More
Research on Psychiatric Disorders Targets Inflammation

August 6, 2014 | JAMA Network
Activation of the immune system is the body’s natural reaction to infection or tissue damage, but when this protective response is prolonged or excessive, it can play a role in many chronic illnesses, not only of the body, but also of the brain. | Read More
Depression May Lower Response to Shingles Vax
February 14, 2013 | MedPage Today
Untreated major depression may hamper the protective effect of varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine against herpes zoster -- shingles -- in older individuals, researchers found. | Read More
Uncovering the Source of Inflammatory Malaise
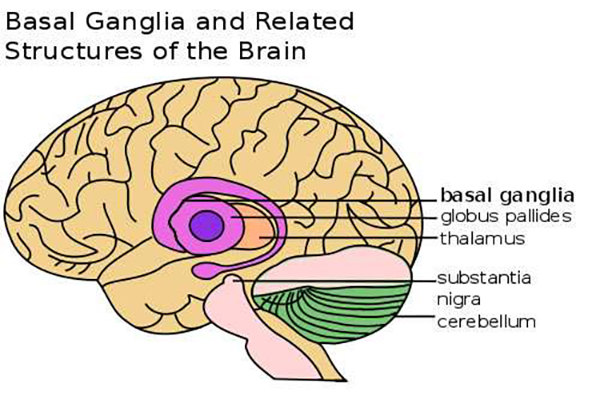
October 22, 2012 | Medical Xpress
A study conducted by researchers at Emory indicates that inflammation targets a part of the brain called the basal ganglia, causing symptoms of depression and fatigue. | Read More
The Evolutionary Advantage of Depression

October 2, 2012 | The Atlantic
More people die from suicide than from murder and war combined, throughout the world, every year. In the United States, suicide recently surpassed automobile accidents as the leading cause of violence-related death, according to a study appearing in the American Journal of Public Health. | Read More
Targeting Inflammation to Treat Depression
September 4, 2012 | Emory University
"Inflammation is the body's natural response to infection or wounding, says Andrew H. Miller, senior author for the study and professor of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences at Emory University School of Medicine. "However, when prolonged or excessive, inflammation can damage many parts of the body, including the brain." | Read More
Why Stress Might Make You Sick
April 2, 2012 | Health Day
A new study involving the common cold may help explain why stress, which dampens the immune system, seems to trigger inflammation in many people. | Read More
Study Shows How Stress Triggers Immune System
January 23, 2012 | US News & World Report
Shedding some light on why stress might be bad for you, a new study finds that parts of your immune system ramp up when you get into personal conflicts with others.
Study Sheds Light on a Potential Cause of Insomnia
June 16, 2010 | Medical Xpress
In a study at Emory University, investigators have shed new light on a potential cause of insomnia, demonstrating that products of the immune system called cytokines may be the culprits. | Read More

