Project 1
Discovery that Toll like receptors are present on enteric neurons and are involved in regulation of ENS development and gastrointestinal motility
Introduction of Research
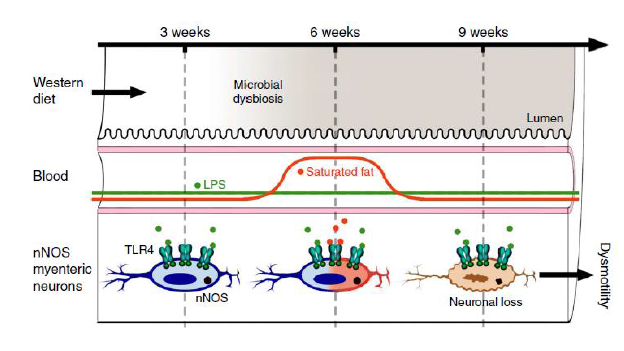
Toll like receptors (TLRs) on enteric ganglia plan an important role in the regulation of enteric nervous system development and regulation of gastrointestinal motility. High fat diet intake can alter gut microbiota leading to the metabolic syndrome, resulting in enteric neuronal degeneration and change gastrointestinal transit.
Associated Publications
a. Anitha M, Vijay-Kumar M, Sitaraman SV, Gewirtz AT and Srinivasan S. Gut microbial products regulate murine gastrointestinal motility via Toll-like Receptor 4 signaling. Gastroenterology, 2012, 143(4): 1006-16, PMID:22732731
b. Nezami BG, Mwangi SM, Jeppsson S,Anitha M, Yarandi S, Farris AB and Srinivasan S. miR-375 mediates palmitate-induced enteric neuronal damage and high-fat diet-induced intestinal dysmotility. Gastroenterology, 2014, 146 (2):473-83, PMID 24507550
c. Mallappa Anitha, François Reichardt, Sahar Tabatabavakili, Behtash Ghazi Nezami, Benoit Chassaing, Simon Mwangi, Matam Vijay-Kumar, Andrew Gewirtz , and S. Srinivasan. Intestinal dysbiosis contributes to the delayed gastrointestinal transit in high-fat diet fed mice, Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, 2016, 2(3):328-339, PMID 27446985
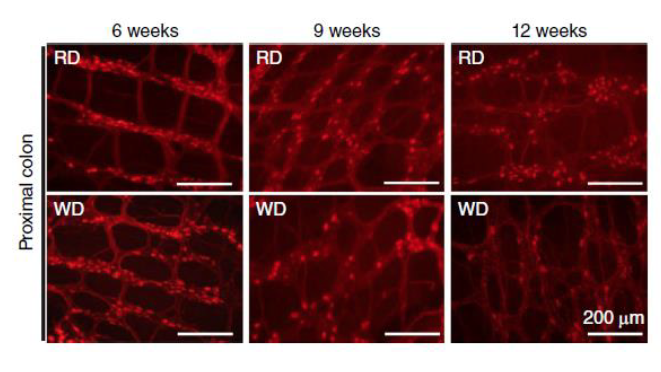
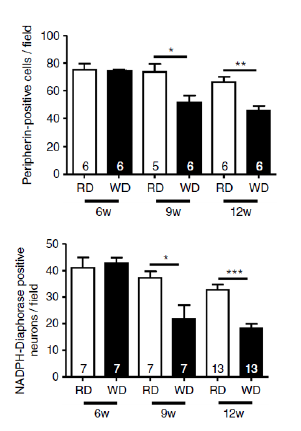
d. Francois Reichardt, Benoit Chassaing, Behtash Ghazi Nezami, Ge Li, Sahar Tabatabavakili, Simon Mwangi, Karan Uppal, Bill Liang, Matam Vijay-Kumar, Dean P Jones, Andrew T. Gewirtz, and S. Srinivasan. Western diet induces colonic nitrergic myenteric neuropathy and dysmotility in mice via saturated fatty acid- and LPS-induced TLR4 signaling. Journal of Physiology, 2017, 595(5):1831-1846
Project 2
Understanding the signal transduction mechanisms of enteric neuronal survival and differentiation
Introduction of Research
Our lab generated an enteric neuronal cell line that is currently being used by many laboratories around the world to study enteric neuronal physiology. We identified some neurotrophic factors and signal transduction pathways regulating ENS function, plasticity and differentiation.
We have teased out the mechanisms of GDNF regulation of enteric neuronal survival and the signal transduction pathways involved. We also established the role of BMP2 in the regulation of enteric neuronal survival.
Associated Publications
a. Mallappa A, Chandrasekharan B, Salgado J, Grouzmann E, Mwangi S, Sitaraman S, Srinivasan S. GDNF modulates enteric neuronal survival and proliferation through Neuropeptide Y. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1164-1178, NIHMS14189. PMCID: PMC2349982
b. Mwangi S, Mallappa A, Fu H, Srinivasan S. GDNF-mediated enteric neuronal survival involves GSK--3-3. Neuroscience 2006;143:241-251. PMID: 16996218
c. Mallappa A, Joseph I, Ding X, Martinez E, Sawchuk M, Mwangi S, Hochman S, Sitaraman SV, Anania FA, Srinivasan S. Characterization of embryonic and post natal enteric neuronal cell lines with restoration of intestinal neuronal function. Gastroenterology 2008;134:1424-1435. PMCID:PMC2612783
d. Anitha M, Shahnavaz N, Qayed E, Joseph I, Gossrau G, Mwangi SM, Sitaraman SV, Greene JG, Srinivasan S. BMP2 promotes differentiation of nitrergic and catecholaminergic enteric neurons through a Smad1 dependent pathway. American Journal of Physiology-Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010;298(3):G375-83. PMID: 20007850
Project 3
Identification of the changes in the enteric nervous system in animal models of diabetes mellitus
Introduction of Research
Our research has led to an understanding of the changes in gastrointestinal motility in diabetes. We have made significant progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying gastrointestinal motility disorders as they relate to diabetes. Our key findings are that we found increased oxidative stress in enteric neurons from human colonic samples supporting a mechanism for diabetic enteric neuropathy and we found novel roles for enteric nervous system (ENS) neurotrophic factors in relation to diabetes. We identified changes in the enteric nervous system in streptozotcin-induced diabetic mice including loss of nitrergic enteric neurons. These changes were reversed in the presence of the growth factor GDNF.
Associated Publications
a. Chandrasekharan B, Anitha M, Blatt R, Shahnavaz N, Kooby D, Staley C, Mwangi S, Jones DP, Sitaraman SV, Srinivasan S. Colonic motor dysfunction in human diabetes is associated with enteric neuronal loss and increased oxidative stress. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2011;23:131-8, e26.
b. Mallappa A, Ghonda C, Sutliff R, Parsadanian A, Mwangi S, Sitaraman SV, Srinivasan S. GDNF rescues hyperglycemia-induced diabetic enteric neuropathy through activation of the PI-3-Kinase/Akt pathway. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2006;116:344-356. Associated editorial: Christopher K. Rayner and Michael Horowitz. Gastrointestinal motility and glycemic control in diabetes: the chicken and the egg revisited? J Clin Invest 2006;116:299-302. PMCID:PMC1359053
c. Christie, Jennifer; Shroff, Sagar; Shahnavaz, Nikrad; Carter, Latoya A.; Harrison, Melanie S., Dietz-Lindo, Karan A.; Hanfelt, John; S. Srinivasan. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial to Examine the Effectiveness of Lubiprostone on Constipation Symptoms and Colon Transit Time in Diabetic Patients. American Journal of Gastroenterology, 2017, 112(2):356-364, PMID 27922028
Project 4
Discovery that gut microbiota can influence metabolic syndrome and obesity
Introduction of Research
In collaboration with Dr. Andrew Gewirtz, we have several observations on the influence of gut microbiota on influencing the metabolic syndrome. We have shown that altered gut microbiota can lead to the metabolic syndrome and a role for dietary emulsifiers in altering gut microbiota leading to metabolic syndrome.
Associated Publications
a. Vijay-Kumar M, Aitken JD, Carvalho FA, Cullender TC, Mwangi S, Srinivasan S., Sitaraman SV, Knight R, Ley RE, Gewirtz AT. Metabolic syndrome and altered gut microbiota in mice lacking Toll-like receptor 5. Science 2010;328:228-31
b. Chassaing, B., O. Koren, J. Goodrich, A. Poole, S. Srinivasan, R. E. Ley and Andrew T. Gewirtz. Dietary emulsifiers alter gut microbiota-intestinal interactions promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome. Nature 5;519(7541):92-6
c. Colonic microbiota encroachment correlates with dysglycemia in humans. Benoit Chassaing, Raja, S, Lewis JF, S. Srinivasan and Andrew Gewirtz, Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2017: 4(2):205-221 PMID 28649593

